Effective Ways to Calculate the Total Area of a Pyramid in 2025
Understanding the area of a pyramid involves not only calculating its surface area but also grasping its geometric properties. In 2025, as we explore pyramid calculations, we will delve into various formulas and methods that are essential for determining the total area, thereby deepening our understanding of pyramid geometry. This article will provide an insightful guide, helping both students and professionals through the detailed processes involved in calculating the total area of a pyramid.
Understanding the Geometry of Pyramids
The first step in calculating the area of a pyramid is understanding its structure. A pyramid consists of a base and triangular faces. The base can be triangular, square, or rectangular, leading to different types of pyramids. The varying bases produce unique calculations, which are crucial to determining the pyramid base area. Each pyramid is defined by its apex, the highest point, and the slant height—from the apex to the base of each triangular face, which plays a critical role in area calculations.
Types of Pyramids
Pyramids can be classified in many ways—most commonly, they are categorized by the shape of their base. The most notable types include the square pyramid, which features a square base, and the triangular pyramid, defined by a triangular base. Each type has a unique pyramid volume formula and surface area equations. For instance, a triangular pyramid area is computed differently than a rectangular pyramid, contributing to the overall variance in calculating total areas of various pyramid shapes.
Key Properties of Pyramids
One of the essential properties of pyramids is that each pyramid exhibits similar geometric relationships. Factors like the slant height of a pyramid and the perpendicular height from the apex to the base play a significant role in deriving formulas for calculating area. The relationship between these heights and the base area is fundamental when deriving the formula for total area, which encompasses both the base and lateral faces of the pyramid.
Visualizing Pyramids in Geometry
Visual representation is critical in understanding pyramids. Utilizing diagrams can aid in comprehending the relationships among the base, heights, and slant heights. The net of a pyramid—comprising the base and the triangular faces—allows for better visualization when calculating the lateral area of a pyramid or the total surface area. Resources like interactive digital modeling can enhance learning outcomes as one visually navigates the geometric relationships pivotal for calculating pyramid area.
Calculating the Area using Formulas
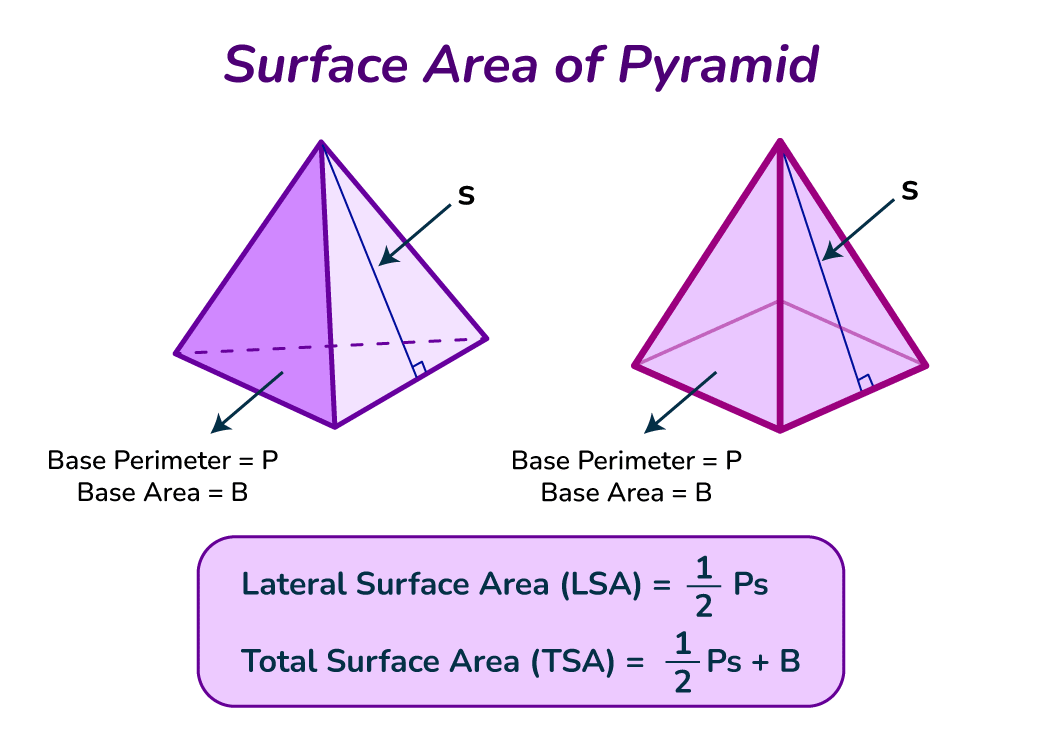
Calculating the total area of a pyramid can be straightforward when using the right formulas. Each pyramid type has specific area and volume equations that facilitate easy calculation. The surface area of a pyramid can be computed by summing the area of the base and the lateral areas of its triangular faces. Let’s break that down for different types of pyramids, including their fundamental formulas.
Square Pyramid Area Formula
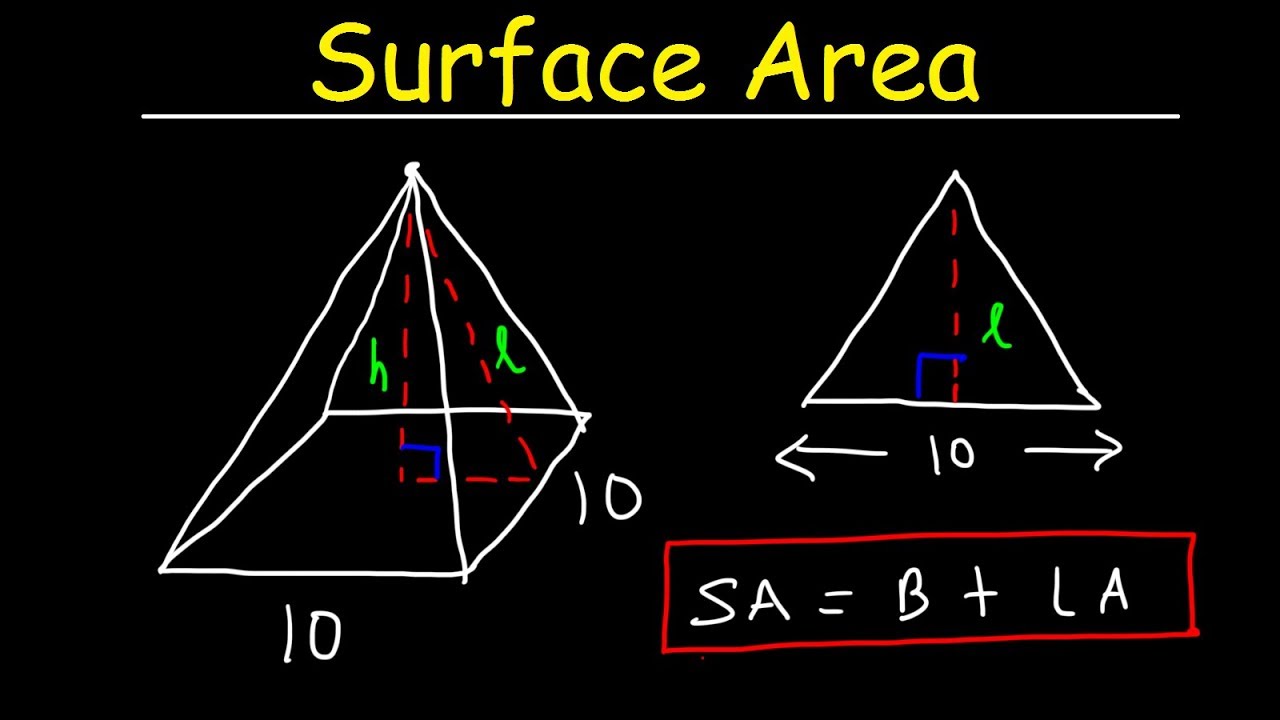
The area of a square pyramid can be computed using the formula: Surface Area = Base Area + Lateral Area. The base area is calculated using the formula for a square, which is Base Area = side². The lateral area, which comprises all four triangular faces, uses the formula: Lateral Area = (1/2) * Perimeter * Slant Height. Thus, understanding how to find the base area calculation is essential in arriving at the total area.
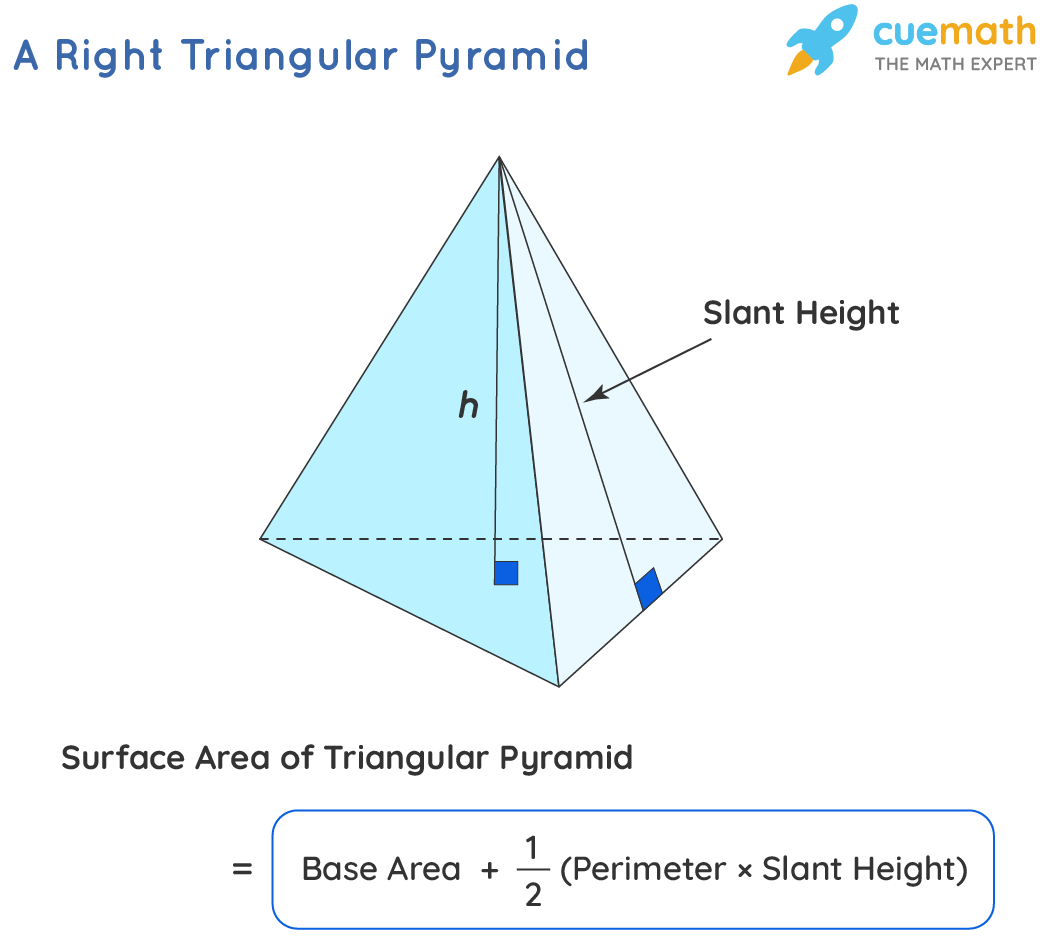
Triangular Pyramid Area Calculation
On the other hand, the area formula for a triangular pyramid involves calculating the triangular base area and the combined areas of the triangular faces. The triangular base can be calculated using the formula for the area of a triangle: Base Area = (1/2) * base * height, and the lateral area can be integrated through the slant height, factoring in each triangular face with its specific area contributions.
Surface Area Implications
The surface area of a pyramid also has practical applications across various fields, including architecture. Understanding how to effectively use the volume formulas for pyramids contributes to comprehensive design principles in construction. Thus, employing surface area implications assists architects and engineers when considering structural integrity alongside aesthetic requirements.
Practical Applications of Pyramid Calculations
Pyramids hold significant importance in both education and real-world applications—ranging from historical architecture to modern geometric principles. A deeper knowledge of pyramid shape calculations can have profound implications in fields such as civil engineering, design, and even environmental science where spatial reasoning and volume calculations are essential.
Geometric Shapes in Real Life
Understanding the total area of a pyramid enables one to maximize space effectively in construction and architectural designs. Whether designing storage facilities or analyzing historical structures, this geometric knowledge serves as a foundation for greater realities in architecture. For instance, the precision needed in estimating the volume of a rectangular pyramid is crucial in determining material requirements and costs.
Educational Resources on Pyramids
As mathematics continues to evolve, various educational resources have emerged to teach students about the importance of pyramids, focusing on their geometric significance. Collaborative learning experiences enable students to explore properties of pyramids hands-on, supported by digital modeling of pyramidal structures to augment their learning experience.
Exploring Historical Significance
Pyramids also have notable historical relevance. From the ancient pyramids of Egypt to modern skyscrapers that leverage similar geometric principles, the understanding of pyramid properties shapes construction methods. Effectively teaching this history alongside geometric calculations can illustrate the enduring significance of pyramid structures in both our past and present.
Key Takeaways
- The area of a pyramid can be calculated using specific formulas based on its base shape.
- Different types of pyramids require different formulas for base area and lateral area calculations.
- Understanding these calculations has practical applications in architecture and engineering.
- Visualization and interactive learning methods enhance the understanding of pyramid geometry.
- Pyramids carry historical and architectural significance that informs design principles today.
FAQ
1. What is the formula for the area of a pyramid?
The formula for the total area of a pyramid combines the base area with the lateral area: Surface Area = Base Area + Lateral Area. Each specific pyramid type may require different base area calculations depending on its shape.
2. How do I calculate the volume of a triangular pyramid?
The volume of a triangular pyramid is calculated by using the formula: Volume = (1/3) * Base Area * Height, where the base area is calculated through the standard triangle area formula: (1/2) * Base * Height.
3. What is the significance of the slant height of a pyramid?
The slant height of a pyramid is critical during area calculations as it is used to compute the lateral area. The slant height extends from the apex down the triangular face to the base edge, aiding in determining surface area and contributing to engineering calculations.
4. How does the base shape affect pyramid calculations?
The shape of the base directly influences both the area and volume calculations of the pyramid. Each base shape (triangular, square, or rectangular) requires specific formulas to reflect its geometrical properties adequately, which must be integrated into the calculations.
5. Can pyramids be applied in practical designs?
Yes, understanding calculating pyramid area has vast applications in architectural designs. For instance, incorporating pyramidal forms in structures can enhance aesthetic appeal while effectively maximizing space, demonstrating geometric principles in real-world scenarios.
For more information and visuals detailing these calculations, you can refer to the illustrations available at the following links: Link 1, Link 2.